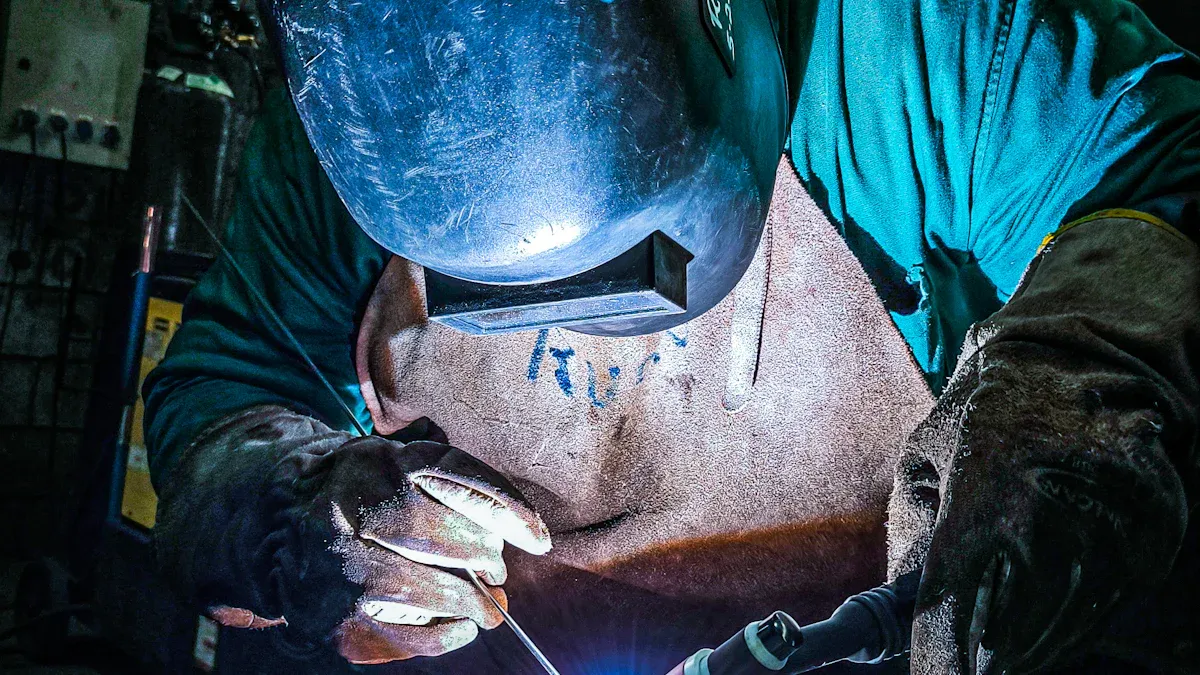
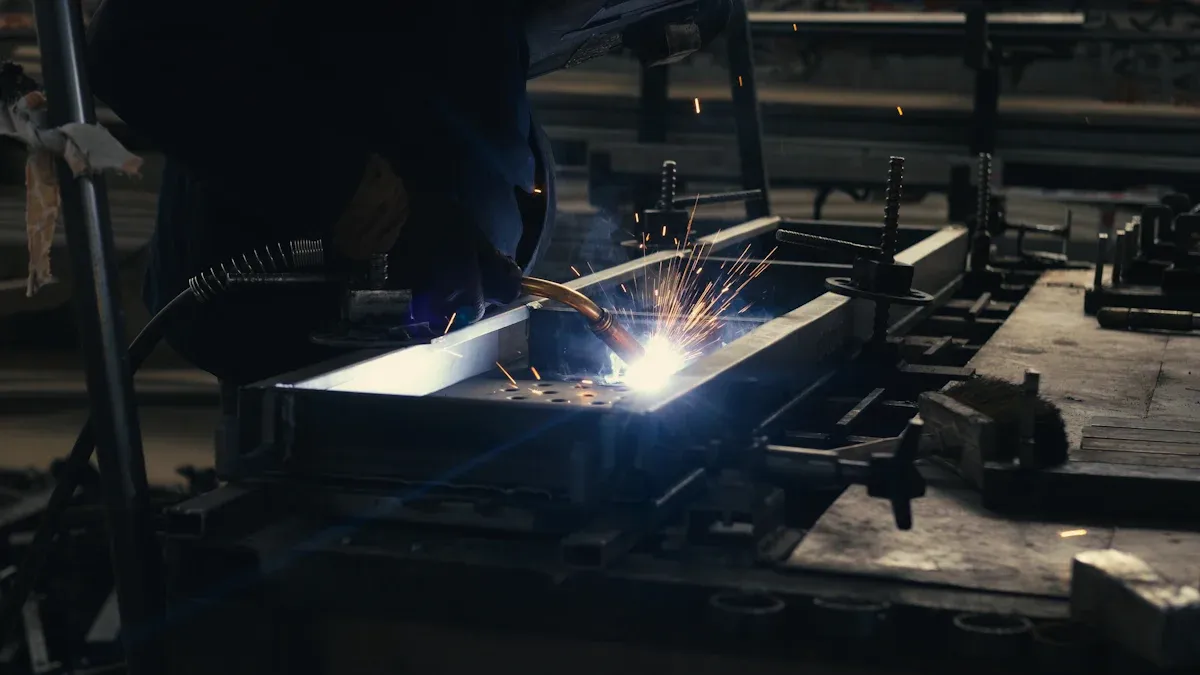
Sheet metal CNC welding uses machines to join thin metal sheets. It makes strong connections and allows for detailed designs. This is perfect for industries needing top-quality work.
Many industries depend on CNC welding because it is fast and flexible. For example:
Car makers use it to build light parts for electric cars.
Builders need sheet metal for roofs and building frames.
Airplane companies need strong and exact parts for safety.
New technology keeps improving sheet metal services. Demand is growing in North America and Asia.
Key Takeaways
CNC welding is important for industries like cars and airplanes. It makes strong and accurate metal connections.
Preparing sheet metal by cleaning and checking for damage is key. This helps create strong and reliable welds.
Choosing the right machine settings and methods, like MIG or TIG, improves quality and saves time.
Checking welds and machines often keeps work safe and problem-free.
Wearing safety gear protects workers from heat, sparks, and bad fumes. This keeps the workplace safe.
Step-by-Step Process of Sheet Metal CNC Welding
Preparing Sheet Metal for Welding
Before welding, the sheet metal must be clean. Dirt, grease, or rust can weaken the weld. I clean the metal with a wire brush or chemical cleaner. If there’s a coating, I remove it to expose bare metal. This helps the welding arc work better.
I also check the metal for bends or damage. Bent sheets can cause bad welds. Clamps or fixtures hold the metal steady. Thin sheets need backing bars to stop burn-through. Good preparation makes stronger welds and prevents problems later.
Tip: Always check the metal’s thickness and type first. Different metals need special welding methods and settings.
Setting Up the CNC Welding Machine
After preparing the metal, I set up the CNC machine. I choose the right torch and electrode for the job. TIG welding uses tungsten electrodes, while MIG welding uses wire electrodes.
Next, I adjust the machine’s settings like voltage and speed. Thin metal needs lower current to avoid overheating. I secure the clamps to keep the metal steady during welding.
Automation is key here. CNC machines reduce mistakes and make consistent welds. Studies show automation lowers costs and improves accuracy. This is important for industries like car manufacturing, where parts must be exact.
Programming the CNC Machine
Programming the CNC machine is the next step. I use software to design the welding path. It includes details like where to start, speed, and angle. The software turns this plan into G-code for the machine to follow.
I check the program for mistakes before using it. Errors can ruin the weld. Once it’s ready, I upload the program to the machine. The machine then welds with perfect accuracy every time.
Using SPC tools helps improve the process. Charts track and fix variations in welding. One study showed SPC tools greatly improved quality and efficiency. Programming and automation make welding faster and better.
Note: Always test the welding program in the software first. This finds problems early and saves time.
Executing the Welding Process
After programming the CNC machine, I start welding. This is where careful planning and setup come together. The machine follows the programmed path to weld accurately.
I keep a close eye on the process. Even though the machine is automated, I check for problems. For example, I watch the arc to make sure it stays steady. If the arc flickers, it might mean the electrode or settings need fixing. If something seems wrong, I stop the machine and adjust it.
Here’s how I handle the welding process step by step:
Start the Machine: I turn on the CNC machine and check its starting point.
Monitor the Weld: I watch the molten metal pool. It should flow smoothly without gaps or splashes.
Adjust Settings if Needed: If the weld looks uneven, I change the voltage or speed.
Finish the Weld: When the machine is done, I check the weld for any visible flaws.
Tip: Always have a fire extinguisher nearby. Safety is very important.
Different welding methods change how this step works. For example, TIG welding needs more care and slower speeds. MIG welding is faster and works well for thicker metal. Spot welding is great for overlapping sheets, while laser welding is best for detailed designs.
Post-Welding Inspection and Finishing
After welding, I check the welds to make sure they are strong. This step is very important because even small flaws can weaken the weld. I inspect the welds by looking at them and using tools like ultrasonic testers to find cracks or holes.
Here’s what I do during inspection:
Visual Check: I look for gaps or uneven spots in the weld.
Measure Accuracy: I measure the parts to make sure they match the design.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): For important jobs, I use NDT tools like X-rays to find hidden problems.
After inspecting, I clean the welds to remove dirt or splatter. I use a wire brush or grinder for this. If the welds need paint or coating, I make sure the surface is smooth and clean.
Note: Cleaning the welds makes them look better and last longer.
Finally, I put the welded parts together to make the final product. This shows why precision is so important in welding. A good weld makes sure all the parts fit perfectly and stay strong.
Tools and Equipment for Welding Sheet Metal
CNC Welding Machines
CNC welding machines are key to modern welding work. These machines make welding precise and consistent. They follow exact instructions, which is crucial for industries like cars and airplanes.
CNC machines boost speed and cut down on mistakes. They move smoothly, keep a steady pace, and make even welds. This improves quality and lowers costs.
When picking a CNC machine, I check if it can handle tough jobs. Machines with smart features save time and need less effort. They also make uniform welds, which is important for big projects.
Welding Torches and Electrodes
Welding torches and electrodes are must-haves for any welder. I pick the torch based on the welding type. For TIG welding, I use tungsten electrodes for clean and accurate welds. For MIG welding, wire electrodes work best for faster jobs.
The torch should be light and easy to hold. This helps me stay steady while welding. I also match the electrode to the metal I’m using. For example, aluminum needs a different electrode than steel. Using the right tools makes welds strong and long-lasting.
Protective Gear and Safety Equipment
Safety always comes first when I weld. I wear gear to protect myself from heat, sparks, and UV rays. My safety gear includes a helmet with a darkening lens, gloves, and a thick apron.
I also wear safety glasses and earplugs to block debris and noise. Good airflow in the workspace keeps harmful fumes away. Having a fire extinguisher nearby is also very important.
High-quality safety gear keeps me safe and focused on my work.
With the right tools and safety equipment, I can weld confidently. From CNC machines to torches and safety gear, each tool helps me create great results.
CNC Programming Software
CNC programming software is very important in welding today. It helps create exact instructions for the CNC machine. The software changes designs into G-code, which guides the machine. Without it, making precise welds for cars or planes would be very hard.
I begin by loading the design file into the software. Most programs accept files like DXF or CAD. After loading, I set the welding path. This includes choosing speed, angle, and weld type. For thin metal, I adjust settings to avoid overheating. The software ensures every detail is correct, especially when using press brake tools to shape metal first.
A helpful feature is the simulation tool. Before using the CNC machine, I test the program virtually. This step finds problems like wrong paths or overlapping commands. Fixing these in the software saves time and materials. It also ensures the weld meets high standards.
The software works well with other tools too. For example, when I use press brake tools to bend metal, I add those sizes into the software. This makes sure the welding matches the shaped parts perfectly. The result is a strong and smooth weld.
Tip: Update your software often. New updates improve accuracy and save time.
Learning CNC programming software is very useful for welders. It makes hard tasks easier and improves work quality. Whether welding small designs or big parts, this software is a must-have tool.
Welding Techniques in Sheet Metal CNC Welding
MIG Welding
MIG welding is a common way to join metals. It’s fast and efficient, using a wire that melts to connect the sheets. This method works best for thicker sheets, from 1 mm to 13 mm. It’s precise and costs between $0.50 and $3.50 per meter.
I use MIG welding for strong and lasting welds. For example, it’s great for car parts that face stress and vibration. It’s also quicker than TIG welding, making it good for big projects. But I watch closely to avoid splatter and keep the weld clean.
TIG Welding
TIG welding is my choice for detailed work. It uses a tungsten electrode for very accurate welds, up to ±0.5 mm. This method is ideal for thin sheets or when a neat finish is needed. Unlike MIG welding, it doesn’t use a melting wire, giving me more control.
I often pick TIG welding for aerospace or electronics jobs needing precision. It’s great for metals like aluminum and stainless steel. Though slower and harder to do, the results are worth it. The welds are smooth, strong, and need little cleanup.
Spot Welding
Spot welding is perfect for joining overlapping metal sheets. It uses two electrodes to press and heat a small area, creating a strong bond. This method works well for materials up to their full thickness. It’s often used in car manufacturing to join layers quickly.
Spot welding is efficient and doesn’t need extra filler material, saving money. However, it’s not for every project. I mainly use it for tasks like building car bodies or metal cases.
Here’s a simple comparison of these welding methods:
Each method has its own strengths. I choose based on the material, thickness, and precision needed for the job.
Laser Welding
Laser welding is a modern way to join sheet metal. It uses a focused laser beam to melt and connect metal pieces. This method is great for thin sheets and detailed designs. The laser’s precision makes strong and clean welds, even for tough tasks.
First, I set up the laser welding machine. The machine creates heat with a powerful laser beam. I adjust the beam’s strength based on the metal’s thickness. For thin sheets, I lower the power to prevent burning holes. The laser is so accurate that it welds small spots without damaging nearby areas.
Here’s why laser welding is useful:
High Precision: It makes neat welds with little bending. This is perfect for electronics and airplanes.
Speed: It works faster than older methods, saving time on big jobs.
Versatility: It works on many metals like aluminum and stainless steel.
While welding, I watch the laser carefully. The beam must stay steady for even welds. If the weld looks uneven, I quickly fix the settings. After welding, I check for problems like cracks using tools like microscopes.
Laser welding is also better for the environment. It creates less waste and uses less energy than other methods. This makes it a smart choice for companies wanting to go green.
Tip: Always wear safety gear when using lasers. The beam can be very dangerous if not handled properly.
Laser welding has changed how I handle tricky designs. Its accuracy and speed make it one of the best welding methods today.
Safety Precautions and Quality Control in Welding
Operator Safety Measures
Safety is the most important part of welding. I wear helmets, gloves, and fireproof clothes to stay safe. Sparks and heat can cause injuries without protection. Good airflow is also very important. Using special tables removes 95% of harmful air particles. This helps prevent breathing problems, which are common in factory jobs.
I follow safety rules to avoid accidents. These include checking risks and setting machine safety limits. Planning the welding steps helps me work in the right position. Workers should report near-misses to find problems early. This stops accidents from happening later.
Equipment Maintenance
Taking care of welding tools keeps them working well. I use clear instructions to maintain machines properly. For example, one guide explains how to clean and fix welding tools. Another guide shows how to adjust machines for accuracy. These steps stop breakdowns and improve welding results.
I write down all maintenance checks to track machine health. Regular inspections help me find worn-out parts early. Fixing broken parts quickly avoids delays and keeps welds strong. Following a repair schedule lets me focus on making great welds without interruptions.
Quality Inspection Protocols
After welding, I check the parts to make sure they are good. I look for cracks or uneven spots on the surface. For important jobs, I use tools like X-rays to find hidden problems. These tests make sure the welds are strong and precise.
I measure the welded parts to see if they match the design. Following inspection rules keeps the work consistent and safe. Workers with good training follow safety steps better, leading to higher-quality results.
By using safety gear, fixing tools regularly, and checking welds carefully, I create projects that are safe and high-quality.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Following industry standards is very important in sheet metal CNC welding. These rules make sure welds are strong, safe, and fit for their purpose. I follow these guidelines to keep my work high-quality and meet customer needs.
Key Standards in Welding
I use rules from groups like the American Welding Society (AWS) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These rules cover materials, welding methods, and inspections. Examples include:
AWS D1.1: Focuses on welding steel structures.
ISO 3834: Ensures quality in fusion welding.
ASME Section IX: Covers welding for pressure pipes and vessels.
These rules help me make safe and reliable welds.
Tip: Always check for updates to these standards. New changes can improve welding quality.
How I Ensure Compliance
I take steps to follow these rules closely:
Training: I learn new skills through workshops and certifications.
Documentation: I write down welding steps and checks to show I follow rules.
Testing: I use tools like scanners and testers to check weld strength.
Benefits of Following Standards
Following these rules helps my work in many ways:
Safety: Welds are less likely to break.
Reliability: Customers trust products that meet these rules.
Efficiency: Clear steps reduce mistakes and save time.
By following these standards, I make sure my welding is safe and high-quality.
Applications of Sheet Metal CNC Welding
Sheet metal CNC welding is used in many industries. It’s precise and efficient, making strong and custom parts. Here’s how it helps three important sectors.
Automotive Manufacturing
Car makers use CNC welding to make strong, light parts. I weld car frames, exhausts, and battery cases for electric cars. CNC machines make sure every weld is safe and meets standards.
This method speeds up production and reduces mistakes. For example:
Charts and tools help find and fix defects.
These tools improve work quality and cut waste.
CNC welding saves time and makes cars safer. Automation has helped meet the demand for electric and hybrid cars.
Aerospace and Defense
Aerospace and defense need very precise and strong parts. CNC welding makes lightweight pieces that handle tough conditions. I weld airplane bodies, missile covers, and satellite parts.
Every weld must be perfect for safety. TIG welding works well for clean and exact joints. Laser welding is great for detailed designs with little bending.
In defense, I’ve welded parts for tanks and ships. CNC welding gives these industries reliable parts for hard tasks.
Construction and Infrastructure
CNC welding is key for building strong structures. I’ve welded steel beams, roofs, and decorative metal for buildings. CNC machines make sure parts fit perfectly, saving time on-site.
This method supports eco-friendly building. It uses less material and energy, helping green projects. I’ve seen more demand for this in city construction.
CNC welding also makes custom designs easy. From tall buildings to old restorations, it creates strong and beautiful results.
Electronics and Consumer Goods
Electronics and consumer goods need precise and fast production. Sheet metal CNC welding helps make strong and detailed parts for these industries. I’ve seen how this technology improves manufacturing and ensures top-quality results.
Applications in Electronics
Welding is important for making electronics like laptops, phones, and appliances. Thin metal sheets are used for cases, heat sinks, and frames. CNC welding makes sure these parts fit well and stay strong. For example, I’ve used TIG welding to join aluminum laptop cases. This method creates neat welds that look good and last long.
Circuit boards also need welding for small metal parts. Spot welding connects these pieces without harming delicate electronics. This method is great for tight spaces and improves devices like tablets and game consoles.
Tip: Use low heat settings when welding electronics. This prevents damage to fragile parts.
Applications in Consumer Goods
Consumer goods like kitchen tools, furniture, and gym equipment benefit from CNC welding. I’ve welded stainless steel for ovens and fridges, making them strong and stylish. MIG welding works fast and creates solid bonds for these items.
Gym equipment, like treadmills and bikes, needs tough frames. CNC welding makes sure they can handle heavy use. I’ve also worked on metal furniture, where laser welding creates smooth joints for a clean look.
Why CNC Welding is Ideal for These Industries
CNC welding has many benefits for electronics and consumer goods:
Precision: It makes accurate welds for small or complex designs.
Efficiency: Automation speeds up work and lowers costs.
Versatility: It works with metals like aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium.
For example, I’ve welded thin sheets for phone cases using CNC machines. The results were perfect, with no mistakes. This level of accuracy is key for products that need to look good and work well.
Note: Keep CNC machines in good condition. This ensures they work properly and produce high-quality welds.
Challenges and Solutions
Welding thin metals can be hard. Too much heat can cause damage or holes. I adjust the machine settings carefully, using lower power and faster speeds. For consumer goods, smooth finishes are very important. Laser welding helps me make clean and polished joints.
By solving these problems, I make sure the products meet industry rules and customer needs.
Sheet metal CNC welding is precise and efficient for strong metal joints. I use a step-by-step process to ensure great results. Proper tools and methods make the work accurate and dependable. Safety gear keeps me safe and improves weld quality. This welding method works well in industries like cars, planes, and electronics. I’ve watched CNC welding turn designs into useful parts, showing its value in today’s manufacturing.
FAQ
What is the best welding method for thin sheet metal?
TIG welding is great for thin sheet metal. It gives accurate control and makes neat, strong welds. This method works well for soft designs and metals like aluminum or stainless steel. Adjust the machine settings to stop overheating or burn-through.
Tip: Use a backing bar to keep thin sheets from bending.
How do I choose the right CNC welding machine?
Pick a machine that fits your project’s needs. For example, laser machines are good for detailed designs, while MIG machines work better for thicker sheets. Check features like automation and metal compatibility before choosing.
Note: Always think about the metal type and thickness first.
Can I weld different metals together?
Yes, but it takes careful planning. Use filler materials that match both metals and adjust the machine settings. For example, welding aluminum to steel needs a special method, like using a transition insert, to make a strong connection.
Tip: Practice on scrap metal first to avoid big mistakes.
How do I ensure safety during CNC welding?
Wear safety gear like helmets, gloves, and fireproof clothes. Good airflow removes harmful fumes. Keep a fire extinguisher close and check equipment often to avoid accidents.
Emoji Reminder: 🛡️ Stay safe! Always use protective gear.
What are common issues in CNC welding, and how do I fix them?
Problems include uneven welds, burn-through, and weak joints. Fix these by changing machine settings like voltage and speed. Cleaning the metal before welding helps too. Regular machine care stops many issues.
Note: Always check welds after finishing to find hidden problems.