Steel processing starts with an important choice: hot-rolled or cold-rolled steel. The main difference is the temperature during production. Hot-rolled steel is made at high heat, which makes it easier to shape. Sheet metal cold roll steel, on the other hand, is processed at room temperature, giving it a smoother surface and more accuracy.
These types of steel are used in many industries worldwide. For example, the construction industry uses hot-rolled steel because it is strong and long-lasting. Things like beams, channels, and plates are key parts of modern buildings. Cold-rolled steel is important in making cars. Its smooth surface looks nice and works well for car sheet metal cold roll steel.
Key Takeaways
Hot-rolled steel is made using high heat. It is easier to shape and cheaper for big projects.
Cold-rolled steel is made at normal temperatures. It has a smooth surface and is more precise, good for visible parts.
Use hot-rolled steel for strong and low-cost uses like buildings and big machines.
Pick cold-rolled steel for projects needing detail and good looks, like car parts and home devices.
Think about your project’s needs, like price, strength, and looks, when choosing between hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel.
What is Hot Rolled Steel?

The Hot Rolling Process
Hot rolling starts by heating steel slabs to very high temperatures, around 1050°C. This heat softens the steel, making it easier to shape. The process has several steps:
Heating Stage: Steel slabs are heated evenly to make shaping easier.
Rolling Stage: The slabs go through rollers, which shape the steel and affect its properties.
Finishing Stage: The steel is rolled again to get the right thickness.
Cooling Stage: On a table, the steel cools and its structure changes.
Coiling Stage: The steel is coiled for storage, which can change its strength.
Tip: Hot rolling is great for making large amounts of steel with steady quality. It’s popular in industries like construction and car-making.
Characteristics of Hot Rolled Steel
Hot rolled steel has unique features that make it different from other steel types:
Surface Finish: Its surface is rough and has scale from the heat.
Strength and Ductility: It is strong and flexible, so it bends easily.
Dimensional Accuracy: It’s less precise than cold rolled steel but works for most uses.
Cost Efficiency: Hot rolled steel costs less because it’s simpler to make.
These features make hot rolled steel useful for many purposes.
Applications of Hot Rolled Steel
Hot rolled steel is used in many industries because it is strong and adaptable. Common uses include:
Construction: It’s used in buildings, bridges, and tall structures. Its strength makes projects safer and faster.
Automotive: It’s found in car frames and truck parts, where strength matters.
Energy Infrastructure: Wind towers and supports use it for its strength and rust resistance.
Marine Engineering: Ships and offshore platforms use it because it resists saltwater damage.
Specialized Applications: LPG tanks use it to handle high pressure safely.
Note: Demand for hot rolled steel is rising worldwide. For example, the market may grow from USD 500 billion in 2024 to USD 700 billion by 2033, thanks to industries like construction and automotive.
What is Cold Rolled Steel?
The Cold Rolling Process
Cold rolling shapes steel at room temperature for smoothness and precision. Unlike hot rolling, it doesn’t use heat but relies on pressure. The process starts with cooled, cleaned hot-rolled steel. This steel is passed through rollers to make it thinner and stronger.
Cold rolling improves the steel’s strength and hardness. It also makes the steel more accurate in size. The surface becomes smooth and free of roughness or scale. This makes it great for projects needing exact measurements and durability.
Tip: Cold rolling is best for things like car panels or appliances where looks and accuracy matter.
Characteristics of Cold Rolled Steel
Cold rolled steel has special features that make it stand out:
Superior Surface Finish: It looks smooth and polished, perfect for visible uses.
Enhanced Strength: The process makes it stronger and harder for tough jobs.
Dimensional Precision: It’s very accurate in size, ideal for precise parts.
Corrosion Resistance: Its smooth surface helps prevent rust, especially with coatings.
The World Steel Association says cold rolled steel is strong and resists rust well. These qualities make it popular in construction and car-making. The market for cold rolled steel is expected to grow from USD 143.26 billion in 2024 to USD 165.02 billion by 2033. This shows the rising need for high-quality steel products.
Applications of Cold Rolled Steel
Cold rolled steel is used in many industries because it is strong, precise, and looks good. Here are some examples:
Automotive Industry: It’s used in lightweight cars and electric vehicles. Parts like body panels and battery cases need its strength and smoothness.
Construction: Builders use it for roofs, walls, and precise structures. Its rust resistance and accuracy make it a top choice.
Home Appliances: Its smooth surface is great for fridges, washers, and other items.
Energy Efficiency: Making cold rolled steel now uses less energy and creates less pollution. Energy use dropped by 14.07%, and CO2 emissions fell by 6.65%.
These energy-saving improvements match the demand for eco-friendly materials.
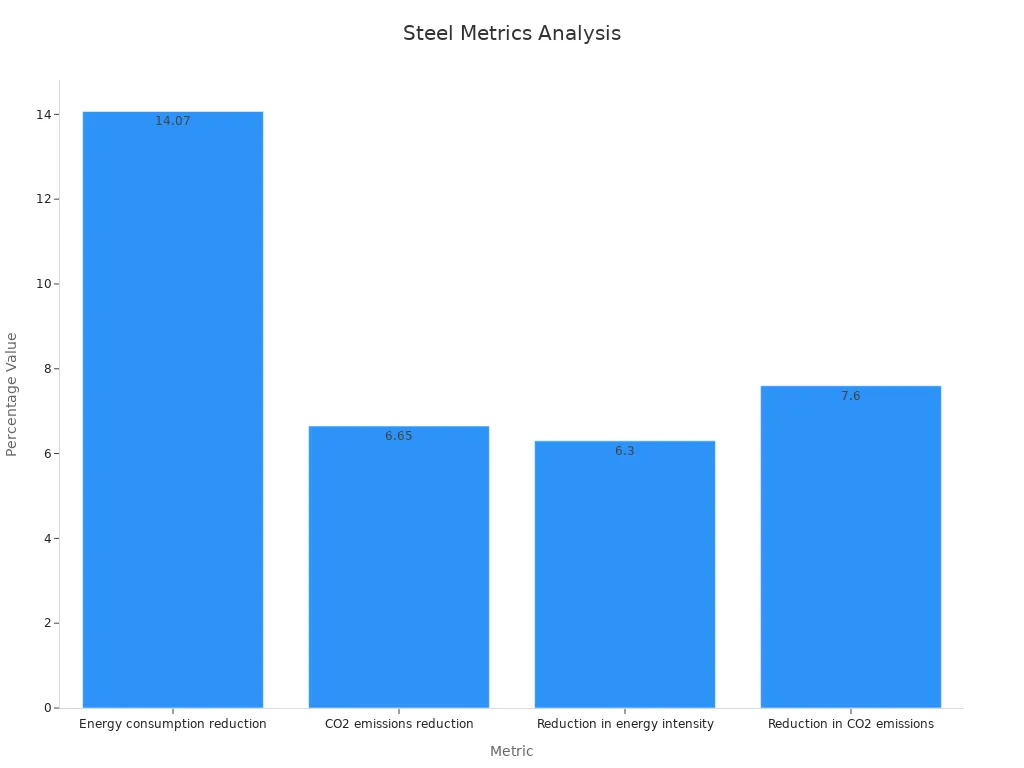
Note: Car makers want lighter materials to meet emissions rules and save fuel. Cold rolled steel is perfect for this while staying strong and reliable.
Hot Rolled vs. Cold Rolled Steel: Key Differences

Cost Comparison
Hot rolled steel costs less because it’s easier to make. The process heats steel and shapes it quickly without extra steps. This makes it great for projects with tight budgets. Cold rolled steel, however, needs more work. It is cooled and rolled precisely, which raises its cost.
If you need smooth surfaces or exact sizes, cold rolled steel is worth the price. But for big projects like building beams or machines, hot rolled steel saves money and stays strong.
Tip: Think about your project’s size and needs before choosing steel.
Strength and Durability
Both types of steel are strong, but they last differently. Hot rolled steel is tough and bends easily, so it’s good for heavy jobs like buildings or car frames. Cold rolled steel is stronger because of how it’s made. It resists bending and holds up under pressure.
Tests show cold rolled steel handles repeated stress better. For example:
AISI 301LN steel has a fatigue strength of 1414.53 MPa, higher than AISI 420 steel.
AISI 301LN also lasts longer under heavy use, making it great for tough jobs.
If your project needs to handle stress or carry weight, cold rolled steel is a smart pick.
Surface Finish
The surface look is a big difference between these steels. Hot rolled steel has a rough, scaly surface from cooling. This makes it less ideal for things where looks matter. Cold rolled steel, on the other hand, is smooth and shiny. It’s perfect for visible parts like car panels or appliances.
Measurements show this difference clearly:
Hot rolled steel has a roughness (Ra) over 3.0 μm, making it uneven.
Cold rolled steel has an Ra under 1.0 μm, giving it a polished look.
If appearance or precision is key, cold rolled steel is the better choice. But for strong structures where looks don’t matter, hot rolled steel works well and costs less.
Applications and Suitability
Choosing between hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel depends on their uses. Each type is best for certain jobs because of its features.
Hot Rolled Steel Applications
Hot rolled steel is great for strong and affordable projects. Its rough surface and flexibility make it useful for tough tasks. It’s often used in:
Structural Components: Beams and frames for buildings and bridges.
Industrial Equipment: Machines needing strength, not exact measurements.
Energy Infrastructure: Wind turbines and pipelines need its toughness.
Marine Engineering: Ships and platforms resist damage from harsh weather.
This steel is best for big projects where looks don’t matter much.
Cold Rolled Steel Applications
Cold rolled steel is ideal for jobs needing precision and smooth finishes. Its polished surface and extra strength make it perfect for:
Automotive Manufacturing: Car panels, battery cases, and light parts.
Home Appliances: Fridges, washers, and other visible household items.
Construction: Roofs and walls that need to resist rust and fit well.
Furniture: Stylish desks, chairs, and cabinets with clean designs.
This steel works well when appearance and accuracy are important.
Suitability for Engineering Projects
Research shows steel choice affects project success. A study of 15 designs found project times varied by steel type (p = 0.02). While team size and effort didn’t matter much, low p-values (p < 0.15) hinted they might still affect results.
Tip: Use cold rolled steel for precise, quick projects. Pick hot rolled steel for strong, budget-friendly ones.
Both types of steel are key in building, engineering, and manufacturing. Your decision should match your project’s needs.
Pros and Cons of Each Type
Advantages of Hot Rolled Steel
Hot rolled steel has many benefits and is budget-friendly. Its making process is simple and quick, lowering costs. It’s great for projects needing lots of steel without losing quality.
Cost Efficiency: Hot rolling is cheaper than cold rolling due to its simplicity.
Production Speed: High heat helps make steel fast for tight schedules.
Versatility: It comes in many types for different uses.
Flexibility: It bends and shapes easily, perfect for building structures.
Note: Studies like "Energy Savings in Hot Rolling" show it uses less energy and works faster with new methods.
Disadvantages of Hot Rolled Steel
Hot rolled steel has some downsides too. Its rough surface and less precise size may not fit detailed projects. Also, it uses a lot of energy, which affects the environment.
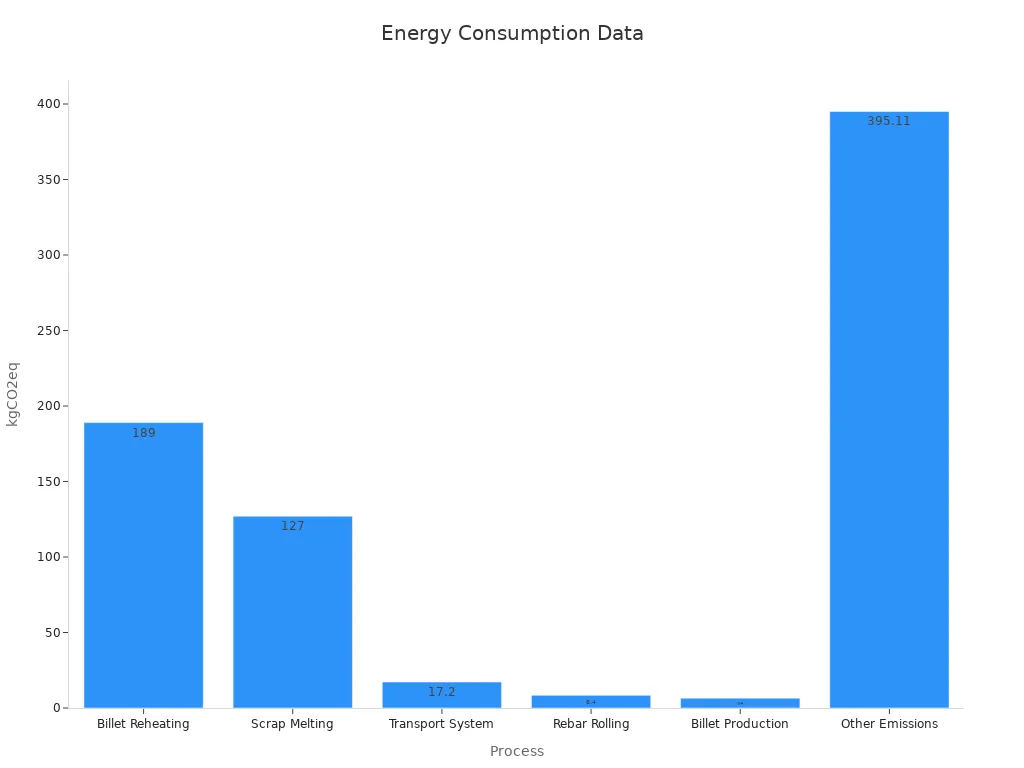
These numbers show how hot rolling impacts the environment, especially in reheating and melting.
Advantages of Cold Rolled Steel
Cold rolled steel is known for its strength and precision. Its smooth look and toughness make it great for jobs needing exact sizes and nice finishes.
Enhanced Strength: Cold rolling makes steel stronger for tough tasks.
Dimensional Accuracy: It’s very precise, ideal for detailed parts.
Aesthetic Appeal: Its shiny surface looks great for visible items.
Corrosion Resistance: Smoothness helps coatings stick, lasting longer.
Cold rolled steel is popular in car-making and building, where looks and performance are key.
Disadvantages of Cold Rolled Steel
Cold rolled steel is strong and precise, but it has some downsides. Think about these before using it for your project.
Higher Cost
Cold rolled steel costs more than hot rolled steel. Extra steps like cleaning and finishing make it pricier. If your budget is tight, this might not be the best choice.
Tip: Pick cold rolled steel only if you need smoothness and exact sizes.
Limited Size Options
Cold rolling works well for thin sheets and small parts. It’s not used for big items like beams or thick plates. For larger steel, hot rolled steel is better.Reduced Flexibility
Cold rolled steel is harder and less bendable than hot rolled steel. It’s not good for projects needing curves or complex shapes.Susceptibility to Stress
Cold rolling adds stress inside the steel. This can cause bending or warping during cutting or welding. Extra treatments, like annealing, may be needed, adding time and cost.
Note: Always check your project’s needs. Cold rolled steel is precise but not ideal for every job.
While cold rolled steel is strong and smooth, its limits make it unsuitable for some projects. Compare its pros and cons to decide what works best for you.
Picking hot-rolled or cold-rolled steel depends on your project. Hot-rolled steel is cheaper and easier to shape. Cold-rolled steel is more exact and looks smoother. Think about cost, strength, and recycling when deciding.
Tools like AHP or TOPSIS help compare these factors. Choose carefully to match the steel to your project’s needs.
FAQ
What is the main difference between hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel?
Hot-rolled steel is made using high heat. This makes shaping easier. Cold-rolled steel is shaped without heat. It has a smooth surface and is more precise.
Which type of steel is better for construction projects?
Hot-rolled steel is strong and affordable. It’s great for building beams and frames. Looks don’t matter much for these parts.
Why is cold-rolled steel more expensive?
Cold-rolled steel costs more because it needs extra steps. These include cleaning, rolling, and finishing. These steps make it stronger and smoother.
Can hot-rolled steel be used for visible parts?
Hot-rolled steel can be used for visible parts. But its rough surface doesn’t look nice. Cold-rolled steel is better for smooth and polished finishes.
How do I choose the right type of steel for my project?
Think about your project’s needs. Hot-rolled steel is good for big, strong structures. Cold-rolled steel is better for detailed and visible parts.






